Ph. D Coursework
Paper – 2 Theory (Language)
Assignment
Preface
English for Specific Purposes (ESP) is one of the approaches to English
language teaching that focuses on the process of learning English language. It
is a subset of teaching English as Second or Foreign language. It is usually
concerned with teaching English to adult learners (university students) or to
the people in professional work situations according to knowledge and the
skills they require for specific work context. ESP generally focuses on a
specific occupation or profession, such as business English, scientific
English, legal English, aviation English, English for medical professionals,
English for waiters, English for tourists, English for hotel receptionist etc.
It is an approach to work with language in the context that emphasizes on
specific linguistic needs of learners. Therefore, the need to understand the
requirements of other professions and willingness to adapt to these
requirements make teaching English for specific purposes more difficult than
teaching English for general purposes. As it requires not only proficiency in
the language but also specific knowledge of that discipline or technical
field.
ESP as a learner-centered approach
ESP emphasis on learners' specific linguistic needs and teach
accordingly which defines the central position of learners. The key defining
feature of ESP is that its teaching and materials are founded on the results of
needs analysis of learners. The questions should be asked before teaching ESP
course is almost like
Why do students want to learn English?
What will be the target situation of language use?
Which skills do they need to master?
Specific needs of the learners can be identified by examining that
situation and the texts (written or spoken) in detail by asking these questions
that help to understand context or discourse through target situation analysis
and discourse analysis.
ESP is usually classified into two main branches: English for academic
purposes (EAP) and English for occupational/ Vocational purposes (EOP/EVP). In
English for academic purposes, English is usually taught in higher education in
order to prepare students to use English language appropriately for
study, like being able to read various reference books or literature available
in English and to write in an academic context. While in English for Vocational
purposes, English is taught in the context of the trades, various
occupations, or professions and investigates how this specialist language is
used in real-world contexts. EVP courses are based on the analysis of specific
communicative needs of the workplaces.
Origin of ESP
ESP has not started as a specific movement but grew out of various
emerging trends around the world. It has rapidly developed around the 1970s to
be a major part in English language teaching and research. Three main reasons
commonly found for the emergence of ESP are as under.
1. The demands of Brave New
World
The expansion of scientific, technical and economic activity at global
level, created the world dominated by two important forces: Technology and
Commerce. Rapid development in these two areas created the need for
International language to communicate with people around the world. Due to the
economic power of the United States over the world in the post war era English
became a global Language. People were crazy about learning English like
businessmen who want to do business deals at international level or students
who want to study in foreign countries or to read texts in English. Because of
this demand, English language teaching became specific in order to fulfil the
needs of the people in different contexts.
2. A revolution in linguistics
At the same time, when demand for specific English courses grew at
international level, new ideas emerged in the study of language. Traditionally
the linguists focus on teaching rules, forms or structures like grammar, but
focus shifted from formal features of language to the actual use of language in
real life communication. With the progress in the areas like science,
technology and commerce gave rise to specific focus on the language used in
various contexts like English for science and technology, Business English
etc.
“Tell me what you need English for, and I will tell you the English that
you need”
This became the guiding principle of ESP that designed their courses by analyzing the individual needs of language learners.
3. Focus on the learner
ESP emerged from the new developments in the psychological aspect of
learning that emphasize on the importance of learners (student centered) and
their attitudes towards the learning language. Through need analysis, it is
found that learners have different interests, needs and demands to learn
English language. Courses have been designed according to those needs and
interests of the learner which increase their motivation to learn language that
is an effective factor in teaching and learning of English.
ESP is centered on the language (grammar, lexis, register), skills (LSRW)
discourse and various genres for which it has developed its own approaches,
materials and distinctive methodology.
Development of ESP
From its early beginning in the 1960s ESP has developed in various
phases, now in its fifth phase.
1.
The register analysis phase - The conception of research
This phase took place in the 1960s and early 1970s, based on the basic
principle of different registers. Register is a special variety of language
used in various fields, contexts and social settings. Register analysis is an
analysis of grammatical and lexical features of the language used for
particular purpose and developed from the principle of ESP that English of a
specific science differs from each other in terms of its grammatical and
lexical features. Then, the syllabus has designed on these linguistic features.
Main motive behind this analysis is pedagogic one to make ESP more relevant to
learners' needs.
2.
The rhetorical or discourse analysis - Beyond the sentence
In this Second Phase, focus shifted on the level above the sentences
that focuses on how sentences were combined in discourse to produce meaning.
The concern of the research is to identify organizational patterns in the text
and then syllabus designed based on these patterns. Teaching materials based on
this approach taught students to recognize textual patterns and discourse
markers.
3.
The target situation analysis - The conception of need
According to Hutchinson and Waters (1987), target situation analysis was
aimed to take student’s responses and set it on a more scientific basis by
establishing procedures to understand learners’ reasons for learning. This
approach helps to design more concrete syllabus based on the needs of various
professions in context of communication purposes, setting, the means of
communication, language skills, functions, structures, etc.
4.
The concept of authenticity - The skills and strategies
The Fourth Stage has been an effort to look below the surface and
consider not language but the thinking process that underlie language use. The
principal Idea behind this skill centered approach is underlying all language
use, having common reasoning and interpreting processes that enable us to
extract meaning from the discourse. A focus on specific subject registers
is unnecessary in this approach because the process is not specific to any
register. In terms of its materials this approach generally puts emphasis on
listening or reading strategies.
5.
A Learning - Centered Approach
ESP concerns language learning rather than language use. In the origin
of ESP, we can identify three forces characterized as need, new ideas about
language and learning. Major concern among these is with language learning and
understanding its process. Language learners have their own experiences on how
language is learnt.
Syllabus Design
While teaching English language for various purposes, most of the
teachers of English language always think about the different methodologies
(methods or approaches) rather than designing concrete/specific syllabus.
Because syllabus design has been a challenging job not only for teachers but
also for the whole education system today. Syllabus must be framed in an
effective way that helps to fulfil the course objectives and intended goals. It
should be practical and applicable enough in the real-world scenario that after
completion of the course students must be able to meet the demands of the
placement. Designing the language syllabus is a very important part of the
language course because it should be specifically designed based on What
and Why students want to learn language.
According to David Nunan, a syllabus design is concerned with selecting
and grading of the content. It is a kind of a roadmap for teachers as well as
for the learners which guide them regarding what and how they will learn in a
particular course. It provides a basic outline regarding some elements or
topics of language that will be covered throughout the course. It also mentions
the student learning outcomes or course objectives that students are expected
to achieve by the end of the course.
Distinction between the Syllabus and Curriculum
A syllabus is usually concerned with the ‘content’, (What to teach) that
will be dealt in a language course. It is more specific than a curriculum
and only one part of it. Content is a single element of the syllabus that
includes need analysis, learning objectives for students, what should be
the weightage of each topic, how the content will be taught, and how it
will be evaluated. Syllabus is simply a statement of what is to be learnt. The
curriculum is more general and broader concept than the syllabus. Jack C.
Richards is of the opinion that curriculum development in language teaching can
be done through seven systematic stages i.e. needs analysis, target situation
analysis, planning learning outcomes, course organization, selecting and
preparing teaching materials, providing for effective teaching, and evaluation.
Some important elements require to design good syllabus
• To study the parameters
essential to present day syllabus design (Skill or competency base)
• To design a need based
& job-oriented syllabus for language learners
• Teachers should have
liberty to design their own syllabus
• Syllabus should be
advanced with updated knowledge about the subject that consider current trends
• It should mention the
classroom requirements
• Need analysis
• It should develop
connection between students and teacher
• Logical arrangement of
the content in the syllabus
• Selection of resource
material and textbooks
• Grading & evaluation
Objectives of syllabus design
• To enable a working
knowledge of language for the students
• To assist meaningful
conversation verbally or non-verbally
• To draft concrete
syllabus as one general syllabus can't suffice or cater the needs of all the
courses
• To satisfy linguistic
needs of the students which are specific and differ from one another (IT,
medical, commerce)
• Due to this multiplicity
of needs, syllabus should be precisely structured for specific purposes with
aim to overcome linguistics complexities
• Learner should acquire sound
knowledge of language and must be able to communicate effectively than just
looking at completion of the course
On what criteria, syllabus be designed?
• Language components
• Target situation and
needs
• Skill based and practical
in nature
• Based on job requirements
• Kind of functions and
tasks perform by students
• Focus on specific
context, discourse and register of language use
Why is the syllabus design more important for ELT courses?
In India, we have heterogeneous classes of learners from different
language backgrounds, cultures and experiences. So, a language teacher requires
a proper directional map (syllabus) to teach language to a diversified group of
learners according to their actual needs. For this, every teacher should look
at syllabus design with utmost importance and seriousness so that it can be
effectively implemented in the heterogeneous classroom with indigenous
syllabus. Many students have experienced the big gap between what they learn in
the classroom and what will be required in the placement. Thus, the
syllabus should be designed in a way that when students go into the market or
society, they should not feel that they have not learned what they must deliver
in the future.
Role of classroom teacher in syllabus design
Generally, teachers are just the consumers (recipients) of other
people's syllabuses and their role is to implement the plans of applied
linguists, governing agencies and so on. Very few teachers have the liberty to
design their own syllabuses. As they are more aware about the actual needs of
the students, set of the topics to discuss in the classroom, level of the
students, teachers should be involved in the process of designing language
syllabus. Teachers are very important stakeholders in education because they
understand how students can acquire skills and knowledge so they can design
their syllabus accordingly. Teachers can be active and successful developers of
the language syllabus, but they are marginalized as they never asked to
participate in the task of syllabus design, even their voice is avoided
when they provide some important suggestions.
Models of Syllabus Design
- Munby’s
Needs Analysis Model
Munby’s approach is partly drawn from the socio-linguistic base for
designing a syllabus and emphasis on the communicative needs of language
learners. It is the most useful model for analyzing linguistic needs to select
and include specific language components in the course. Communicative Needs
Processor (C. N. P.) is the heart of the model that helps to identify what
learners want to do with language. The model includes relevant categories as
following,
1.
Purposive Domain - this category helps to identify the
specific purpose and type of ESP. e. g. educational: science and technology,
communications studies, law, medical etc in Higher Education
2.
Setting - the time and place. e.g. -
lecture rooms, tutorials, seminars, library, laboratories, art rooms, examinations
3.
Interaction - the roles in which the participants
will find themselves in terms of status, age group, social relationships
etc. e.g. student relationships: student-student, student-lecturer
/tutor/ teacher technician
4.
Instrumentality: a. medium of communication.
1. e.g. spoken -
receptive and productive
a. written - receptive
and productive.
b. channel of
communication.
2. e.g. face to face,
print, audio-visual
5.
Dialect - the dialects the student will have
to understand and produce. e.g. standard American accents and dialects.
6.
Target level - level of linguistic proficiency,
different skills may be different. e.g. ELTS
7 for Law, JMB grade 3 etc.
7.
Communicative event - what the learner
will have to do with English. e.g. attend
lectures, take part in seminars, write paper, give presentation etc.
8.
Communicative key - the way communication needs to be
carried out. e.g. formal/informal
plus range of attitudes.
9. Profile - what the student needs to be able to do.
Bell's Model
This model offers a first approximation to language teaching syllabus
design as shown shown in following diagram
It includes external requirements (of markets) that evaluates errors
made by the learners to specify their level in learning process, student's
present competence that focus on skills and abilities that learners have and
educational philosophy. The main emphasis in the present situation is on the
student's present competence which includes needs analysis, skills analysis,
and syllabus design.
Cook's Multi-competence Model
Multi-competence considers the ability of a person having knowledge of
two or more than two languages in a single mind. It mentions that people who
know more than one language have different minds than people who know only one
language because it affects the first language and way of thinking of the
people. These multicompetent individuals should be called "L2 '' rather
than 'second language learners' because they are learning a new language (native
speakers are not considered as first language learners). The aim of L2
learning should be to become a multi competent user of more than one language,
and not imitate the native speaker of that language. Cook has argued with
evidence that knowledge of more than one language can change the way people
think.
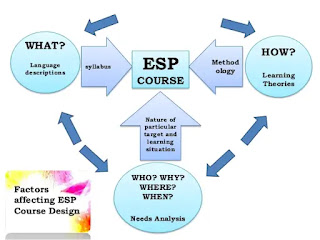
Importance of syllabus design in English for specific purposes
'I keep six honest serving-men
(They taught me all I knew);
Their names are What and Why and When
And How and Where and Who'
(Rudyard
Kipling)
Syllabus design has an important role in ESP courses as it is
designed to meet the specific requirements of the market. ESP syllabus (course)
should be designed carefully because it enables learners to perform specific
tasks. To design an EPS course, we need to ask questions in order to understand
the reasons why students want to learn English. Above mentioned lines
indicated the need to ask questions for detailed information and clarification
regarding objectives behind learning English. Kipling’s ‘six honest
serving men' can help us to outline the basic questions like
Why do students need to learn English? (Purpose)
Who is going to be involved in the learning process? (Teachers,
students)
Where and when learning takes place? (Target situation)
What does the student need to learn? (Language aspects)
How does learning happen? (Methodology)
To know the answers to these questions, needs analysis can be used as an
approach to design a specific syllabus as it is the main cornerstone in the
procedure of ESP syllabus design. Professionalism, Practicality and Specialization are three key words of major focus in teaching English for
specific purposes. These keywords should be taken into consideration while
designing various ESP syllabuses which suits various professions in which
students want to pursue their career, secondly it should be practical and
applicable enough that will help the students to acquire skills and knowledge
required in that field and third thing that syllabus should be more specific to
learners as general syllabus can't satisfy heterogeneous learners. Vocabulary,
register, discourse, context are distinctive elements found in different
ESP courses like business, science and technology, engineering and so on. These
elements of language should be taken into consideration in designing concrete
syllabus. There are various approaches for teaching English language but for
teaching English for specific purposes the most appropriate and used approach
today is the Communicative or Functional approach that deals with various
functions or purposes for which learners use English. For example, the English
for the functions like to greet, ask, suggest, complain and so on. Similarly,
English used in various professions is quite different for the people in hotel
management, tourism, journalism, mass communication and many others. These all
professions used a distinct form of English that is unique in discourse,
context, register and lexis.
Conclusion
Thus, syllabus design is a very important part or stage in designing any
language courses which generally preceded by need analysis which is the base or
important pillar on which ESP syllabus is designed to fulfil expectations of
the market as well as learners. So, ESP syllabus should be carefully designed
with the valuable contribution and participation of classroom language teachers
as they are more aware about learners, their attitudes, level of understanding,
strengths and weaknesses in language components and their future communicative
needs.
References
Bell, Roger T. An Introduction
to Applied Linguistics. New York : St. Martin's Press, 1981.
Gillett, A J. "Designing an
EAP Syllabus: English Language Support for Further and Higher
Education." Journal of Further and Higher Education (1989):
92-104.
Hutchinson, Tom and Alan Waters. English
for Specific Purposes : A learning-centered approach. New York: Cambridge
University Press, 1987.
Nunan, David. Syllabus Design.
Ed. C N Candlin and H G Widdowson. Oxford University Press, 1988.
Paltridge, Brian and Sue Starfield,
The Handbook of English for Specific Purposes. Wiley-Blackwell : A
John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
Raza, Asif Ali. "Esp
syllabus." n.d. SlideShare.
<https://www.slideshare.net/AsifAliRaza/esp-syllabus>.
"Vivian Cook (linguist)."
n.d. Wikipedia.
<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vivian_Cook_(linguist)>.



No comments:
Post a Comment